In today’s dynamic digital landscape, the customer journey is no longer a linear path from awareness to conversion. Instead, it has evolved into a complex, multi-touchpoint experience that requires a deep understanding and strategic mapping to drive successful outcomes. This blog will delve into the intricacies of the modern customer journey, exploring how businesses can effectively map the path to conversion in a world where touchpoints are numerous and varied.
Introduction: The Changing Landscape of the Customer Journey
Traditionally, the customer journey was viewed as a straightforward funnel: potential customers would move from awareness to consideration, and finally to decision and purchase. This linear model, however, has been rendered obsolete by the advent of digital technologies and the proliferation of online and offline touchpoints. Today’s consumers interact with brands across multiple channels and devices, leading to a more fragmented and intricate journey.
The Rise of Multi-Touchpoint Interactions : Customer Journey
The modern customer journey is characterized by multiple touchpoints, which can include social media interactions, email marketing, website visits, in-store experiences, online reviews, and more. These touchpoints do not occur in a set sequence; instead, customers may move back and forth between stages, influenced by various factors along the way.
The Importance of Understanding the Customer Journey
For businesses, understanding this evolving customer journey is crucial for several reasons:
- Personalization: Tailoring experiences to meet the specific needs and preferences of customers.
- Optimization: Identifying and improving key touchpoints to enhance the overall journey.
- Efficiency: Allocating resources effectively to maximize return on investment.
- Loyalty: Building stronger relationships with customers by providing seamless and engaging experiences.
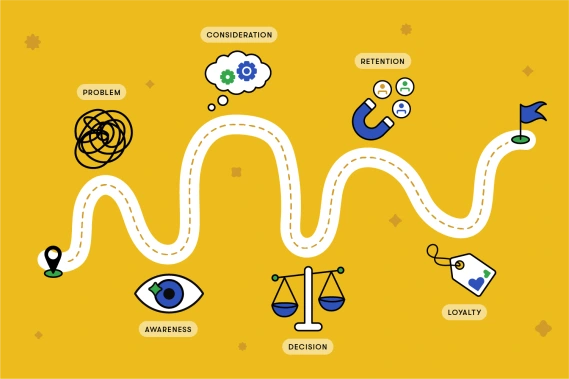
Key Components of the Modern Customer Journey
1. Awareness
The journey begins when a potential customer becomes aware of a need or problem and discovers a brand that could provide a solution. Awareness can be sparked through various channels, such as:
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn play a significant role in brand discovery.
- Search Engines: Organic search and paid advertisements on search engines help brands appear when customers are looking for solutions.
- Content Marketing: Blog posts, videos, podcasts, and infographics that address relevant topics can attract attention.
2. Consideration
Once aware of a brand, the customer moves into the consideration phase, where they evaluate different options. This stage involves:
- Research: Customers gather information about the brand and its offerings through reviews, testimonials, and case studies.
- Comparison: They compare products or services against competitors to find the best fit for their needs.
- Engagement: Interactions with sales representatives, attending webinars, and participating in live chats can influence decision-making.
3. Decision
The decision stage is where the customer decides to purchase a product or service. Key factors influencing this decision include:
- Pricing: Competitive pricing and promotional offers can sway customers.
- Value Proposition: The unique benefits and features of the product or service.
- Trust: Established through positive reviews, strong brand reputation, and transparent communication.
4. Purchase
The purchase phase is the culmination of the journey, but it is not the end. Key elements in this stage include:
- User Experience: A smooth, hassle-free purchasing process, whether online or in-store.
- Payment Options: Offering multiple, secure payment methods to cater to different preferences.
- Post-Purchase Communication: Sending confirmation emails, shipping updates, and follow-up surveys.
5. Post-Purchase
The journey continues post-purchase, focusing on retention and loyalty. Important aspects include:
- Customer Support: Providing timely and effective support to address any issues or queries.
- Feedback: Collecting and acting on customer feedback to improve products and services.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing programs to reward repeat customers and encourage referrals.
Mapping the Multi-Touchpoint Customer Journey
Mapping the customer journey involves identifying and analyzing the various touchpoints a customer interacts with. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively map the customer journey:
Step 1: Define Your Customer Personas – Customer Journey
Understanding your target audience is the foundation of journey mapping. Create detailed customer personas that include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, location, etc.
- Behavioral Traits: Purchasing habits, preferred channels, etc.
- Pain Points: Common challenges and needs.
Step 2: Identify Key Touchpoints
Identify all possible touchpoints across the customer journey. These touchpoints can be categorized into:
- Digital Touchpoints: Website visits, social media interactions, email campaigns, online ads, etc.
- Physical Touchpoints: In-store visits, events, direct mail, etc.
- Human Touchpoints: Customer service interactions, sales consultations, etc.
Step 3: Map the Customer Journey
Create a visual representation of the customer journey by plotting out the touchpoints in sequence. This map should highlight:
- Stages: Awareness, consideration, decision, purchase, and post-purchase.
- Touchpoints: All interactions at each stage.
- Customer Emotions: The emotional state of the customer at each touchpoint.
- Pain Points: Challenges or obstacles the customer may encounter.
Step 4: Analyze the Journey
Evaluate the journey map to identify opportunities and challenges. Focus on:
- Bottlenecks: Points where customers drop off or experience frustration.
- High-Value Touchpoints: Interactions that significantly influence the customer’s decision.
- Gaps: Missing touchpoints or areas where the customer experience can be improved.
Step 5: Optimize the Journey
Implement changes to enhance the customer journey based on your analysis. Strategies may include:
- Personalization: Tailoring content and interactions to individual customer needs.
- Streamlining: Simplifying processes to reduce friction.
- Enhancing Touchpoints: Improving high-value touchpoints to maximize their impact.
Step 6: Monitor and Iterate
Continuously monitor the customer journey and gather feedback to make ongoing improvements. Utilize analytics and customer feedback to:
- Track Performance: Measure key metrics such as conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and retention.
- Identify Trends: Stay ahead of changing customer behaviors and preferences.
- Iterate: Regularly update and refine the journey map to keep it relevant and effective.
Tools and Technologies for Journey Mapping
Leveraging the right tools and technologies can significantly enhance your ability to map and optimize the customer journey. Some of the key tools include:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRM systems like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM help track and manage customer interactions across various touchpoints, providing a holistic view of the customer journey.
Analytics Platforms – Customer Journey
Analytics platforms like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and Mixpanel offer insights into customer behavior, identifying which touchpoints are most effective and where improvements are needed.
Journey Mapping Software
Specialized journey mapping tools like Smaply, Lucidchart, and Microsoft Visio enable businesses to create detailed and interactive journey maps.
Marketing Automation Platforms
Tools like Marketo, Eloqua, and Pardot automate marketing tasks, ensuring timely and personalized interactions at various touchpoints.
Case Studies: Successful Journey Mapping
Case Study 1: Amazon
Amazon’s customer journey mapping is a prime example of leveraging data and technology to create a seamless experience. By analyzing customer behavior across various touchpoints, Amazon has optimized its processes to provide personalized recommendations, streamlined purchasing, and efficient customer support.
Case Study 2: Starbucks
Starbucks uses journey mapping to enhance customer loyalty through its rewards program. By understanding the touchpoints that matter most to their customers, such as mobile ordering and in-store experiences, Starbucks has created a cohesive and engaging journey that encourages repeat business.
Case Study 3: Airbnb
Airbnb’s journey mapping focuses on both hosts and guests, ensuring a positive experience for both parties. By identifying key touchpoints such as booking, check-in, and reviews, Airbnb has optimized its platform to facilitate trust and satisfaction.
Challenges in Mapping the Multi-Touchpoint Customer Journey
Despite its benefits, journey mapping comes with its own set of challenges:
Data Silos
Data is often scattered across different systems and departments, making it difficult to get a unified view of the customer journey.
Dynamic Customer Behavior – Customer Journey
Customer behavior is constantly changing, requiring businesses to continuously update and refine their journey maps.
Integration
Integrating various tools and technologies to create a seamless mapping process can be complex and resource-intensive.
Personalization at Scale
Delivering personalized experiences at scale requires significant investment in technology and data analytics.
Future Trends in Customer Journey Mapping
The future of customer journey mapping will be shaped by several emerging trends:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning will play a crucial role in analyzing customer data and predicting behavior, allowing for more accurate and dynamic journey mapping.
Omnichannel Integration
As customers continue to interact with brands across multiple channels, seamless integration of online and offline touchpoints will become increasingly important.
Real-Time Personalization
Real-time data and analytics will enable businesses to deliver personalized experiences at every touchpoint, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer-Centric Approach
A shift towards a more customer-centric approach, focusing on delivering value and building relationships rather than just driving conversions.
Conclusion: Navigating the Multi-Touchpoint World
Mapping the path to conversion in a multi-touchpoint world requires a deep understanding of the modern customer journey. By defining customer personas, identifying key touchpoints, and continuously optimizing the journey, businesses can create seamless and engaging experiences that drive conversions and foster loyalty.
Embracing the right tools and technologies, and staying ahead of emerging trends, will be crucial for success in this ever-evolving landscape. Ultimately, the
key to thriving in a multi-touchpoint world lies in a customer-centric approach that prioritizes understanding and meeting the unique needs of each customer.

Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!Raise blog range