What is Canonical Tags in SEO?: When it comes to search engine optimization (SEO), one of the lesser-known yet extremely important elements is the canonical tag. Often overlooked by beginners, canonical tags play a critical role in preventing duplicate content issues and ensuring your website’s SEO performance remains strong. In this blog, we’ll explore what canonical tags are, why they matter, and how to use them effectively. We’ll also address common questions about canonical tags in our FAQ section.
What is a Canonical Tag in SEO?
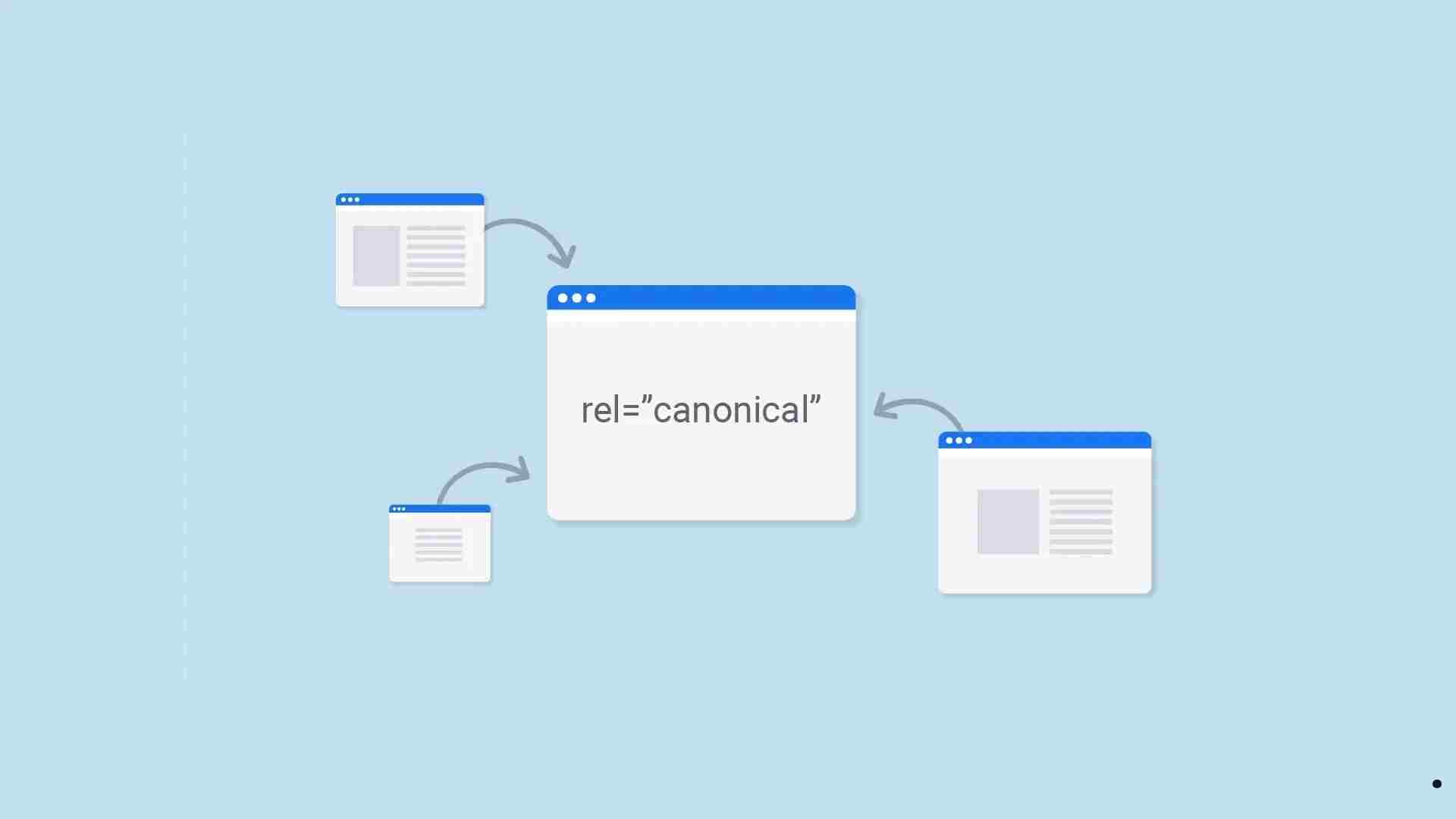
A canonical tag is a snippet of HTML code that helps search engines understand the preferred version of a webpage when multiple versions with similar or duplicate content exist. By using the canonical tag, you can specify the “primary” or “original” URL that search engines should index and rank.
For example:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page">
This code tells search engines that “https://www.example.com/preferred-page” is the canonical or primary version of the page.
Why Are Canonical Tags Important in SEO?
- Prevent Duplicate Content Issues: Duplicate content can confuse search engines, leading to lower rankings or pages being excluded from the search index. Canonical tags consolidate the ranking signals to the preferred URL.
- Consolidate Link Equity: When multiple URLs share the same content, backlinks can get distributed among them. Canonical tags help consolidate link equity to a single URL, boosting its ranking potential.
- Enhance User Experience: By specifying the preferred version of a page, you guide users to the correct URL, avoiding confusion caused by multiple versions.
- Simplify Crawling and Indexing: Search engines have a limited crawl budget for each site. Canonical tags ensure search engine bots focus on the most important pages, improving overall crawl efficiency.
- Maintain a Consistent URL Structure: Canonical tags allow you to maintain a clean and consistent URL structure across your website, which is crucial for both users and search engines.
How to Use Canonical Tags Correctly
- Identify Duplicate or Similar Content: Look for pages with similar content, such as category pages, filtered product pages, or session-based URLs. Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can help identify duplicate content.
- Add the Canonical Tag: Insert the canonical tag into the
<head>section of the HTML code for duplicate or alternate pages. Ensure the tag points to the preferred URL. - Cross-Domain Canonicalization: If your content appears on other websites (e.g., syndicated articles), use cross-domain canonical tags to attribute the original source.
- Avoid Self-Referencing Canonical Tags in Some Cases: While self-referencing canonical tags are often recommended for clarity, avoid using them unnecessarily on pages that don’t have duplicates.
- Test and Monitor: Regularly check if the canonical tags are implemented correctly using tools like Google Search Console, Moz, or Yoast SEO.
- Combine with Hreflang for Multilingual Sites: If your website targets multiple languages or regions, use canonical tags alongside hreflang tags to avoid duplicate content across different language versions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Pointing Canonical Tags to Non-Existent URLs: Always ensure the canonical URL is valid and live.
- Using Different Canonical Tags for Similar Content: Be consistent to avoid confusing search engines.
- Ignoring Mobile and AMP Pages: Use canonical tags correctly to link between desktop, mobile, and AMP versions of your content.
- Overusing Canonical Tags: Not every page needs a canonical tag. Use them where duplicate or similar content exists.
- Forgetting to Update Canonical Tags After URL Changes: If you update a URL, ensure the canonical tags are updated accordingly.
Best Practices for Canonical Tags
- Canonicalize Paginated Content: For long articles or product lists spread across multiple pages, canonicalize the main page unless pagination signals are needed.
- Canonical Tags for E-commerce Sites: Use canonical tags for product variations or filtered pages to prevent duplicate content issues in e-commerce websites.
- Avoid Canonical Loops: Ensure the canonical chain is not circular, where A points to B and B points back to A. This confuses search engines.
- Canonical Tags for Dynamic URLs: Dynamic parameters in URLs can create duplicates. Use canonical tags to point to the static, preferred version.
FAQs: What is Canonical Tags in SEO?
1. Can I use canonical tags for different domains?
Yes, canonical tags can point to a preferred URL on a different domain. This is useful for syndicated content or if you own multiple websites.
2. What is the difference between 301 redirects and canonical tags?
A 301 redirect permanently redirects users and search engines to a new URL. A canonical tag, on the other hand, signals the preferred version of a page without redirecting users.
3. Do canonical tags affect rankings?
Indirectly, yes. By consolidating ranking signals and preventing duplicate content, canonical tags help improve the SEO performance of the preferred URL.
4. Can I use canonical tags with pagination?
No, canonical tags are not suitable for paginated series. Instead, use the rel="next" and rel="prev" attributes for pagination.
5. How do I check if my canonical tags are working?
You can inspect your pages using browser developer tools or SEO audit tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Google Search Console.
6. What happens if I don’t use canonical tags?
Without canonical tags, search engines might index multiple versions of the same content, leading to duplicate content issues and diluting your ranking potential.
7. Can canonical tags point to a URL with different content?
No, canonical tags should only point to a URL with the same or very similar content. Pointing to unrelated content can confuse search engines.
Conclusion
Canonical tags are an essential tool for maintaining a healthy and efficient SEO strategy. By correctly implementing them, you can avoid duplicate content penalties, consolidate link equity, and improve your website’s visibility in search results. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced SEO professional, understanding and using canonical tags effectively is key to optimizing your website’s performance.
Have more questions about canonical tags? Drop them in the comments below, and we’ll be happy to help!
Add a Comment